Heat Capacity of Calorimeter
Heat capacity and calorimetry. For this experiment the calorimeter used is a simple thermos jar and cover.

Constant Volume Calorimetry For More Precise Work Than The Coffee Cup Calorimeter The Heat Capacity Of The Entire C Coffee Cups Chemistry Education Chemistry
A simple calorimeter just consists of a thermometer attached to a.

. Calculating the heat capacity of a calorimeter. Temperature of cold water C Temperature of hot water C 20 920 Volume of cold water mL 990 Volume of hot water mL 950 Final temperature after. After solving this equation for C the heat capacity of the calorimeter can finally be determined as follows.
HEAT CAPACITY OF A CALORIMETER INTRODUCTION LABORATORY SIMULATION A Lab Data - X Check your volume measurement. Therefore we will split the water heat capacity into its mass and the specific heat capacity - that is Cwater mwater Cswater. The operation is based on the change in temperature of a.
4 Find the heat capacity of the calorimeter. Calorimeters can be used to measure the change in heat energy. ΔT where ΔT T final - T initial.
This is the currently selected item. Ccal qcal Δtcold 4184 in J g-1 C-1 X m1 m2 in g --------------eq 4 The unit of heat capacity is J C-1. The amount of heat depends on the heat capacity of a calorimeter.
The heat capacity of the calorimeter C cal is determined by dividing q cal by the temperature change. Energy of phase changes. 8368 J 150 C 558 J C.
125 mathrmkJ of heat was absorbed by the surroundings. In the previous article we discussed the specific heat capacity of substances. Heat capacity divided by the moles of a given substance.
The specific heat of water is 1 calCg. A measure of the thermal energy in a system. Q m.
Did you report your data to the correct number of significant figures. Two Useful Calorimetry Equations. Sign in and order today.
Transfer of energy that results in the change of temperature. It means that it takes a heat of one calorie to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius. 3 The calorimeter got the rest.
During a calorimetry experiment some heat will be absorbed by the calorimeter itself. 33472 25104 8368 J. Heat loss by the fuel is equal to the heat gained by the water.
We get mass of ice. The specific heat capacity of silver is 024 Jg. Q m.
C pc Specific heat capacity of calorimeter 04 J g C ΔT fall in temperature of water and calorimeter 32-5 27C m i mass of ice in gram L latent heat capacity of ice 330 Jg δT rise in temperature 5 C by substituting all the values. The hardware is SET and is what it is but the water component is variable because we can put different amounts of water in the calorimeter. Such measurements can be made easily with this.
The vessel is filled with water and the fuel is burned leading to the heating of the water. Calculate the energy required to raise the temperature of 1500 g of Ag from 273K to 298K. The quantity of heat absorbed by the calorimeter q cal can be determined.
13 C c w m 2 T 2 T m T m T. Say in a calorimeter a fixed amount of fuel is burned. What is the heat capacity of a calorimeter.
Q 400 g 150 C 4184 J g 1 C 1 q 25104 J. Ad 3B Scientific Supply For Science Medical Patient Education Today. Calculate the calorimeter constant if 250 g of water at 600 C was added to 250 g of water at 250 C with a resulting temperature of 350 C.
In the international system they are 4186 JgºC. The heat capacity of the calorimeter accounts for the heat absorbed by the thermometer as well as the heat absorbed by the actual calorimeter. For this experiment the calorimeter used is a simple thermos jar and cover.
The heat capacity of the calorimeter accounts for the heat absorbed by the thermometer as well as the heat absorbed. Heat capacity divided by the mass of a given substance. The three most common types of calorimeters are.
The exact heat capacity is calculated by the CAL3K every 6 seconds after the Start record parameter during a calibration and then saved to the vessel as a Bomb Factor. I found this by using the mcat formula and the specific heat capacity of water 418 Jg C. A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity.
Q m Δt C p. Q m. The heat capacity of calorimeter Ccal is the quantity of heat absorbed by the calorimeter for every one degree rise in temperature of reaction and can be determined by the following formula.
Differential scanning calorimeters isothermal micro calorimeters titration calorimeters and accelerated rate calorimeters are among the most common types. The Heat capacity is a measurement which describes the amount of energy heat needed to raise the vessel temperature by 1 degree. Ad Complete your research with 300000 products.
So our equation above now expands to this. The heat capacity of the calorimeter Ccal is determined by dividing qcal by the temperature change. Calculating the heat capacity of a calorimeter.
Q 950 mathrmg times.
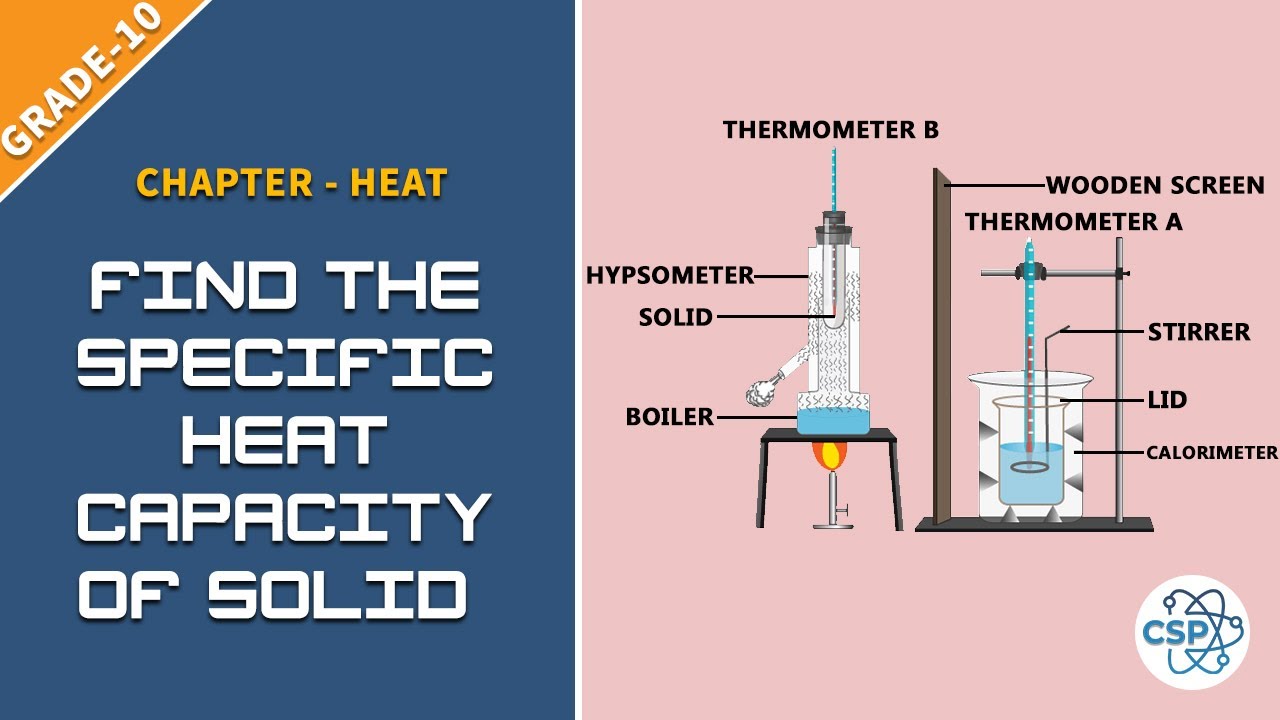
To Find The Specific Heat Capacity Of Solid By Using Method Of Mixtures See Class 10 Physical Properties Heat Science Experiments
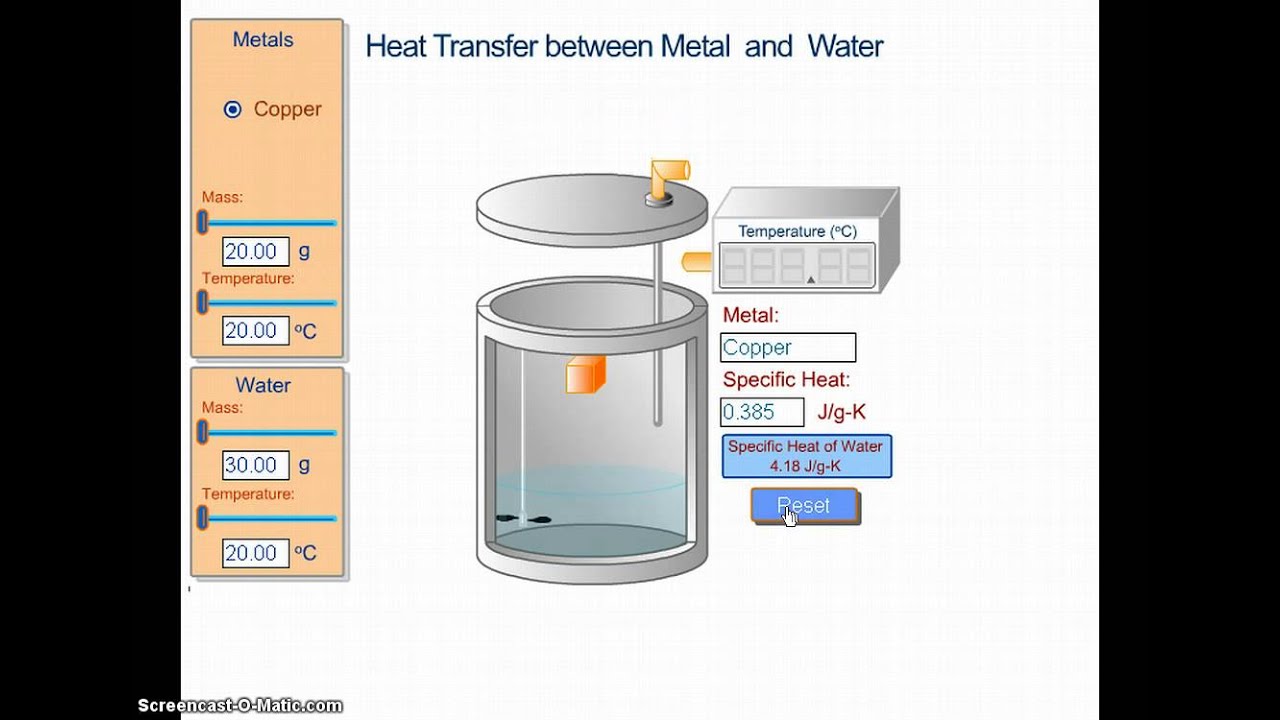
Specific Heat Of A Metal Lab Youtube Science Chemistry Chemistry Class Chemistry Labs

Pin By Redacted On Chemistry Education Chemistry Education What Is Science Ap Chem

Specific Heat Capacity Physics Lessons Science Teaching Resources Science Facts
0 Response to "Heat Capacity of Calorimeter"
Post a Comment